The top 5 most common vulnerabilities in the “UZ” national segment over the past 3 monthsData identified by the UZCERT service in the third quarter of this year
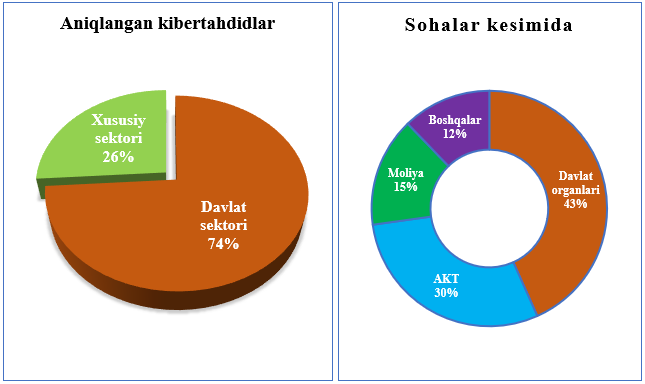
As a result of monitoring conducted by UZCERT in the third quarter of this year, more than 500,000 cyber threats and vulnerabilities were analyzed in the national segment of the Internet. In particular, 410,724 cyber threats were detected in the public sector and 144,705 in the private sector.
During this period, the total number of cyber threats detected in organizations (by industry) – (43%) belongs to state bodies and organizations, (30%) to telecommunications operators and providers, (15%) to the banking and financial sectors.
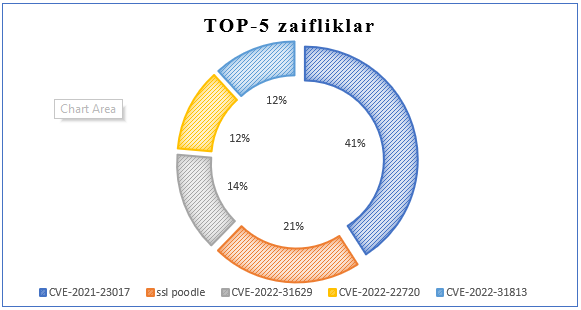
The following “TOP-5” most common vulnerabilities in the server and network devices of state organizations are: “CVE-2021-23017,” “SSL POODLE,” “CVE-2022-31629,” “CVE-2022-22720” and “CVE-2022-31813.” Such vulnerabilities were identified in 138 government agencies and organizations, and recommendations for their immediate elimination were sent to the relevant organizations by the UZCERT service.
CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) is a list of known vulnerabilities in software that can be used by attackers to attack computer systems. Each vulnerability in the list has a unique ID number, and recommendations, patches, or instructions from the developers are provided for self-remediation. The CVE Vulnerability List helps developers and users quickly find and fix vulnerabilities to protect their systems from attacks.
CVE-2021-23017 — Whitespace error when processing DNS responses
(off-by-one error), a network attacker may be able to exit the field, overwriting the least significant byte of the next “heap block metadata”. This can lead to remote code execution in some cases. The highest risk of this vulnerability is to data confidentiality and integrity, as well as system availability.
SSL POODLE (Padding Oracle On Downgraded Legacy Encryption) —
Security vulnerability in SSL 3.0 (Secure Sockets Layer) protocol discovered in 2014. This vulnerability allows attackers to compromise SSL 3.0 encrypted communication and steal confidential information.
CVE-2022-31629 — In PHP versions (before 7.4.31, before 8.0.24
and before 8.1.11) is a moderate vulnerability found. Through this vulnerability, a network or same-site attacker could create an insecure cookie in the user’s browser. In PHP applications, this “Cookie” is mistakenly treated as “__Host” or “__Secure-cookie”, which can lead to security errors, such as stealing cookies or “manipulating” data.
CVE-2022-22720 is a vulnerability in Apache HTTP Server (versions 2.4.52 and earlier). If the server does not correctly reject the body of the request, this can lead to an attack called “HTTP Request Smuggling”.
Through this, hackers manage to “manipulate” requests between the client and the server.
CVE-2022-31813 is a vulnerability in Apache HTTP Server that
this allows an attacker to bypass IP-based authentication by ensuring that “X-Forwarded-*” headers are not forwarded to the origin server. This vulnerability affects Apache HTTP Server versions 2.4.53 and earlier. The vulnerability could allow attackers to bypass IP-based security restrictions.
To address the above cyber threats and vulnerabilities, it is recommended to do the following:
- introducing additional security measures, for example, strengthening security by increasing network security and configuring firewalls, regular monitoring using security tools, and analyzing electronic logs, to prevent potential threats early detection of risks and effective measures against them;
- use of current versions of operating systems and software, constant monitoring and implementation of updates.