Botnets: Hidden Threats
Botnets are hidden threats to modern internet security, posing one of the main sources of cyberattacks. In recent years, botnets have become a danger to major companies, government agencies, and even ordinary users. This article provides a detailed explanation of how botnets work, their various types, the risks they present, and how to combat them.
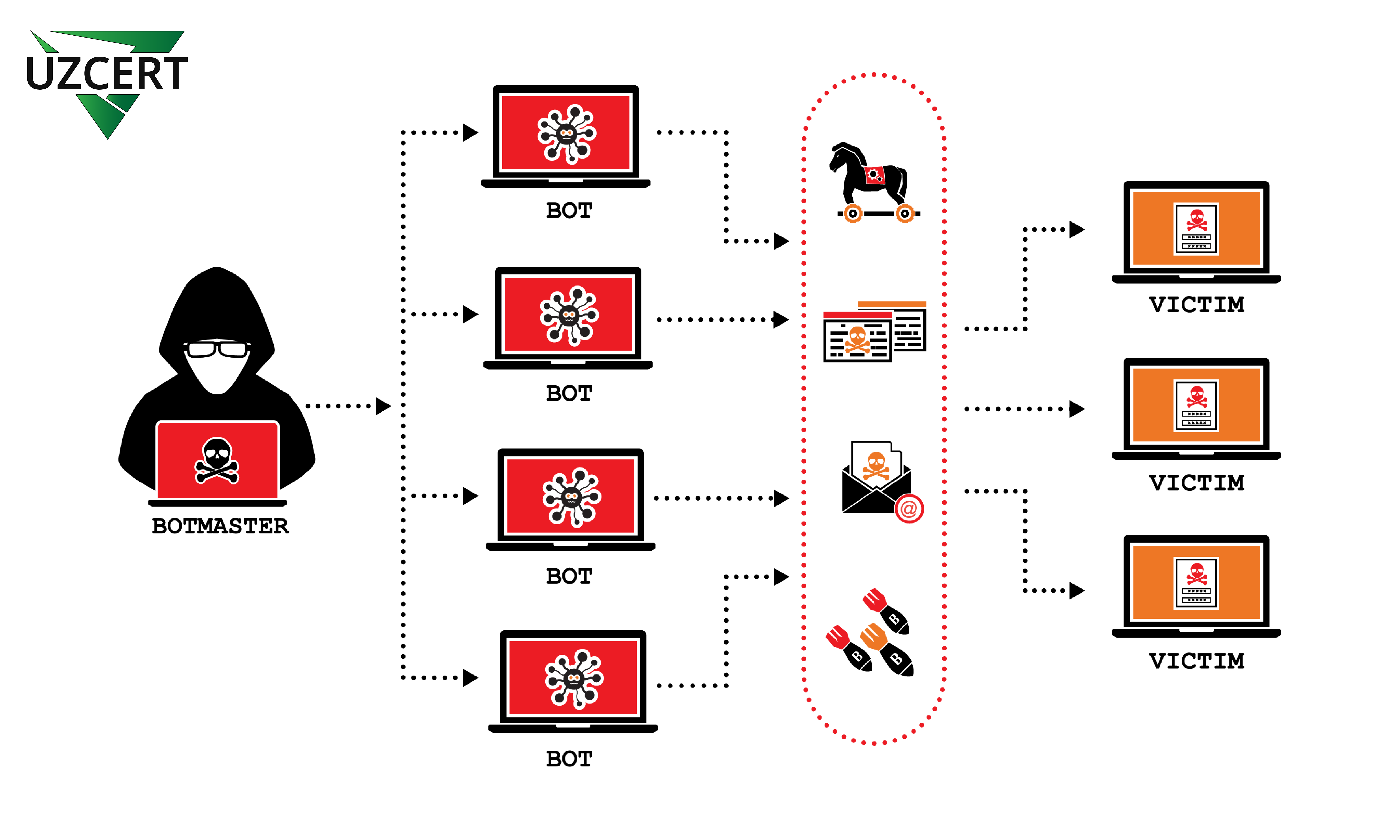
The word “botnet” is a combination of the words “bot” and “network,” representing a network of infected devices. Cybercriminals infect devices (computers, servers, or even “smart” devices) and control them based on commands from the master controller (botmaster). The main goal of a botnet is to control a network for performing specific tasks and using it without the users’ knowledge.
To create a botnet, cybercriminals first distribute malware to users’ devices. This malware, known as “bots,” links the devices to central control after infiltrating them. A botmaster can control all infected devices through their central server.
Bots are typically managed in two main ways:
- Centralized Control (C&C – Command and Control): In this system, all bots are connected to a central control server. The botmaster sends commands to bots through this server.
- Peer-to-peer (P2P): In this system, bots communicate with each other, eliminating the need for a central server. P2P botnets are harder to detect and destroy.
There are various types of botnets used for different purposes:
- DDoS Botnets: The main goal of these botnets is to disable target devices or websites through DDoS attacks. A botmaster uses such botnets to attack various websites or services.
- Spam Botnets: These botnets are used to send a large number of spam messages to users. Spam botnets often send emails with ads, phishing, or malware.
- Banking Botnets: These are specifically designed to steal banking data. Such botnets aim to steal users’ login details, passwords, and other personal information.
- Mining Botnets: Botnets that use computational power to mine cryptocurrency. A botmaster uses users’ computers or servers for cryptocurrency mining, generating income.
Main risks from botnets include:
- Denial of Service (DDoS attacks): Using botnets, cybercriminals can direct large amounts of traffic to a single target, causing a website or service to go offline. This can lead to financial losses and damage to a company’s reputation.
- Privacy Violations: Banking botnets are used to steal users’ confidential information, which can lead to financial losses and the spread of personal information.
- Cryptocurrency Mining: Botnets secretly use infected devices to mine cryptocurrency, increasing electricity costs and reducing device performance.
There are several effective methods to protect against botnets:
- Protection Against Malware: Users and organizations should use powerful antivirus programs and regularly update them.
- Firewall and IDS/IPS Systems: Firewall and Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) can detect and stop botnet attacks. IDS detects attacks, while IPS reports and blocks them.
- DNS Filtering: DNS filtering can prevent connections to botnet command servers, hindering bots from connecting to control servers.
- Network Monitoring: Increasing network monitoring is essential to detect botnet attacks or malicious traffic. Monitoring allows for detecting suspicious activity and taking necessary measures.
- User Awareness: Regular training on malware and phishing attacks helps increase users’ vigilance in security.
Botnets are a hidden but serious threat in the modern internet, becoming an effective tool in cybercriminals’ hands. With them, dangerous actions such as DDoS attacks, data theft, and malware distribution are carried out. To prevent botnets, organizations and users should take security measures, protect their networks, use security software, and raise awareness. As the botnet threat continues to grow, not only is technical protection important in combating them, but also raising user awareness and performing regular updates.