A New Vulnerability Detected in Windows CLFS Driver (CVE-2024-49138) Poses a Serious Threat to System Security
A vulnerability identified in the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) driver, CVE-2024-49138, represents a significant risk for Windows systems. This zero-day vulnerability enables attackers to gain SYSTEM-level privileges without user interaction. It is particularly dangerous for Windows 11 (23H2) systems.
The CVE-2024-49138 vulnerability falls under the Elevation of Privilege (EoP) category and arises due to a heap-based buffer overflow (CWE-122). The Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) has rated this vulnerability with a high severity score of 7.8.
Exploiting the vulnerability requires local access, with a low level of attack complexity. This makes it a substantial risk, especially for organizations with insufficient security measures.
Attackers can exploit this vulnerability by crafting malicious CLFS log files. With local privileges, they can take advantage of the buffer overflow in the CLFS.sys driver, execute arbitrary code, and gain full control of the system. This could lead to unauthorized data access and further exploitation within the organization’s network.
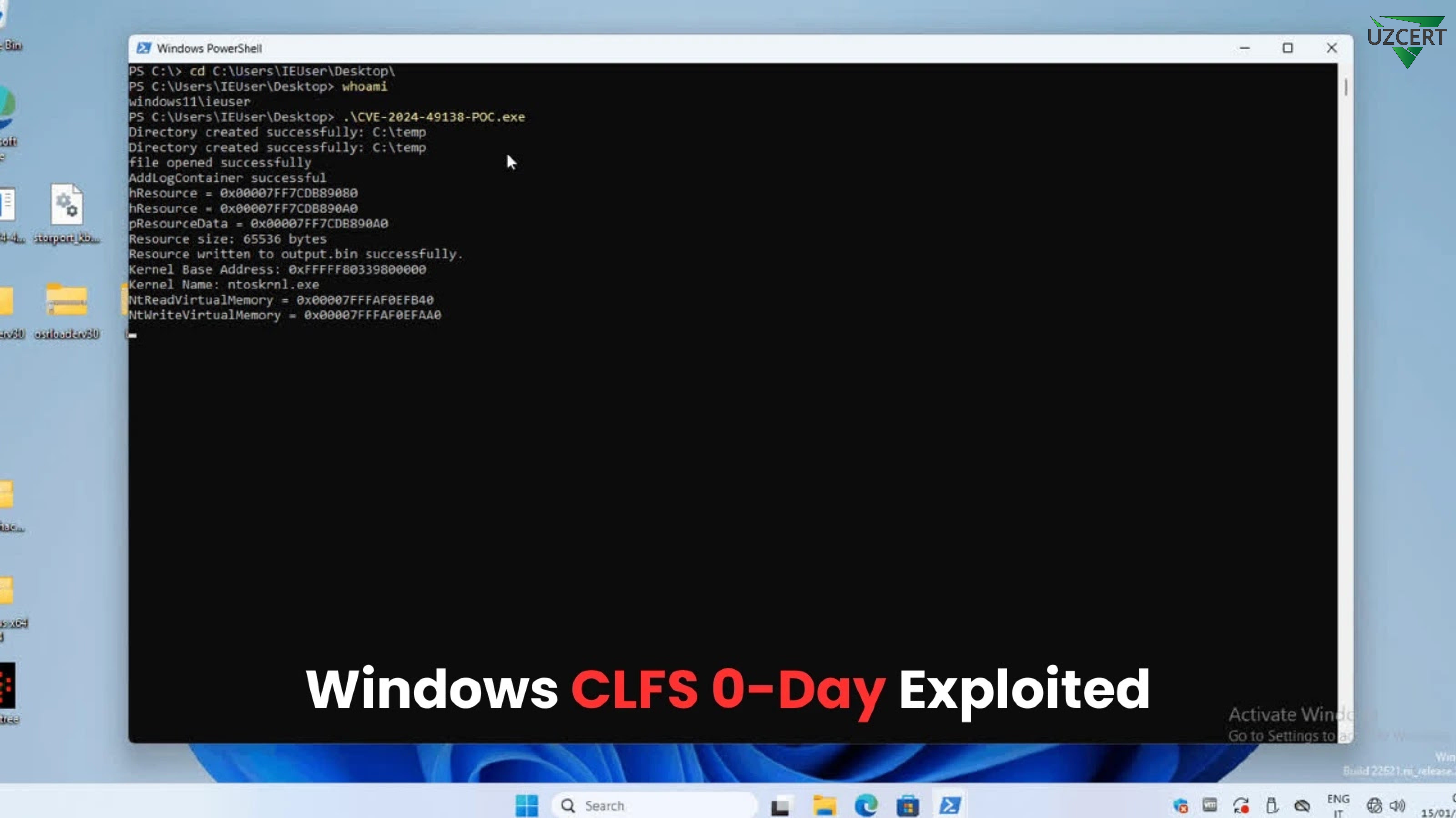
The effectiveness of exploiting CVE-2024-49138 has been confirmed by security researcher MrAle_98. The exploit has been successfully tested on Windows 11 version 23H2 and leverages the buffer overflow vulnerability in the CLFS.sys driver.
In response to this threat, Microsoft released security updates as part of the December 2024 Patch Tuesday. Organizations are strongly advised to take the following actions:
- Install Security Updates: Ensure all relevant updates are applied without delay.
- Review System Configurations: Align system configurations with Microsoft’s security best practices.
- Monitor for Indicators of Compromise: Analyze system logs for suspicious activities related to privilege escalation attempts.
The CVE-2024-49138 vulnerability is a critical threat that requires immediate action from IT departments worldwide. Regular system updates and strengthened security measures are key to effectively combating such threats. Additionally, organizations must maintain continuous monitoring of their networks and actively work to enhance their security posture.



