
A new Android malware called “Ajina.Banker” is attacking users via Telegram to steal banking credentials.
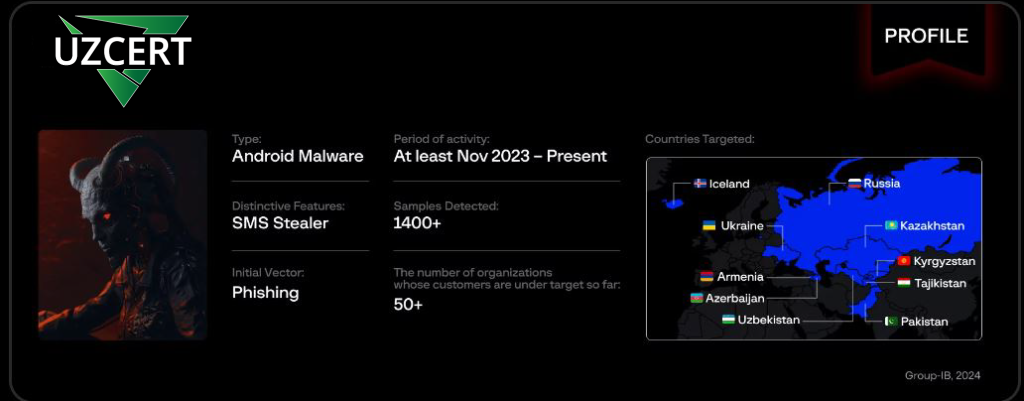
Central Asia has become the target of a new malicious Android malware campaign called Ajina.Banker. This malware was discovered in May 2024. Ajina.Banker has been distributed to users since November 2023, and researchers have identified about 1,400 unique variants of the malware.
Ajina.Banker targets ordinary users by masquerading as trusted applications such as banking services, government portals, and daily utilities, “increasing the infection rate and luring people to download and run the malicious file, thereby compromising their devices.”
The malware is mostly spread through social engineering tactics on messaging platforms like Telegram. Hackers create many software applications to distribute malicious links and files disguised as attractive offers, promotions, or even local tax authority applications. Lured by promises of “profitable work” “earn rewards” or “claim your achievements,” users unknowingly download and install malware, putting their devices at risk.
Attackers also take advantage of the user’s interest to send messages with only a malicious file attached.
Ajina used themed messages and localized advertising strategies to create a sense of urgency and excitement in regional community chats, encouraging users to click links or download files without suspecting malicious intent.
Although it is mainly aimed at users in Uzbekistan, Ajina.Banker’s reach extends beyond the borders. The malware collects information about financial apps installed from various countries, including Armenia, Azerbaijan, Iceland, and Russia. In addition, it collects SIM card data and incoming Blocks text messages, potentially 2FA code for financial accounts.
Malware has a level of adaptability. Newer versions showcase additional features, including the ability to steal user-supplied phone numbers, bank card details and PINs.
To protect yourself and your devices from “Ajina.Banker” and similar threats, beware of unwanted messages and downloads of various files, download software products from trusted sources such as Google Play Store, carefully check when accessing software applications , install security software and stay up-to-date on the latest malware threats and the latest security updates.



