A Dangerous Vulnerability Found in React and Next.js: PoC Release Sparks Global Concern
Millions of websites and web applications around the world rely on React and Next.js. Therefore, the discovery of a new vulnerability — CVE-2025-55182 — has caused serious concern among developers. The flaw enables remote code execution (RCE) on the server and has received the highest severity score — CVSS 10.0.
The vulnerability affects React versions 19.0.0–19.2.0, as well as Next.js versions 15 and 16. Most notably, even if an application does not directly use server functions, it remains vulnerable if React Server Components (RSC) are enabled.
What Did the PoC Exploit Demonstrate?
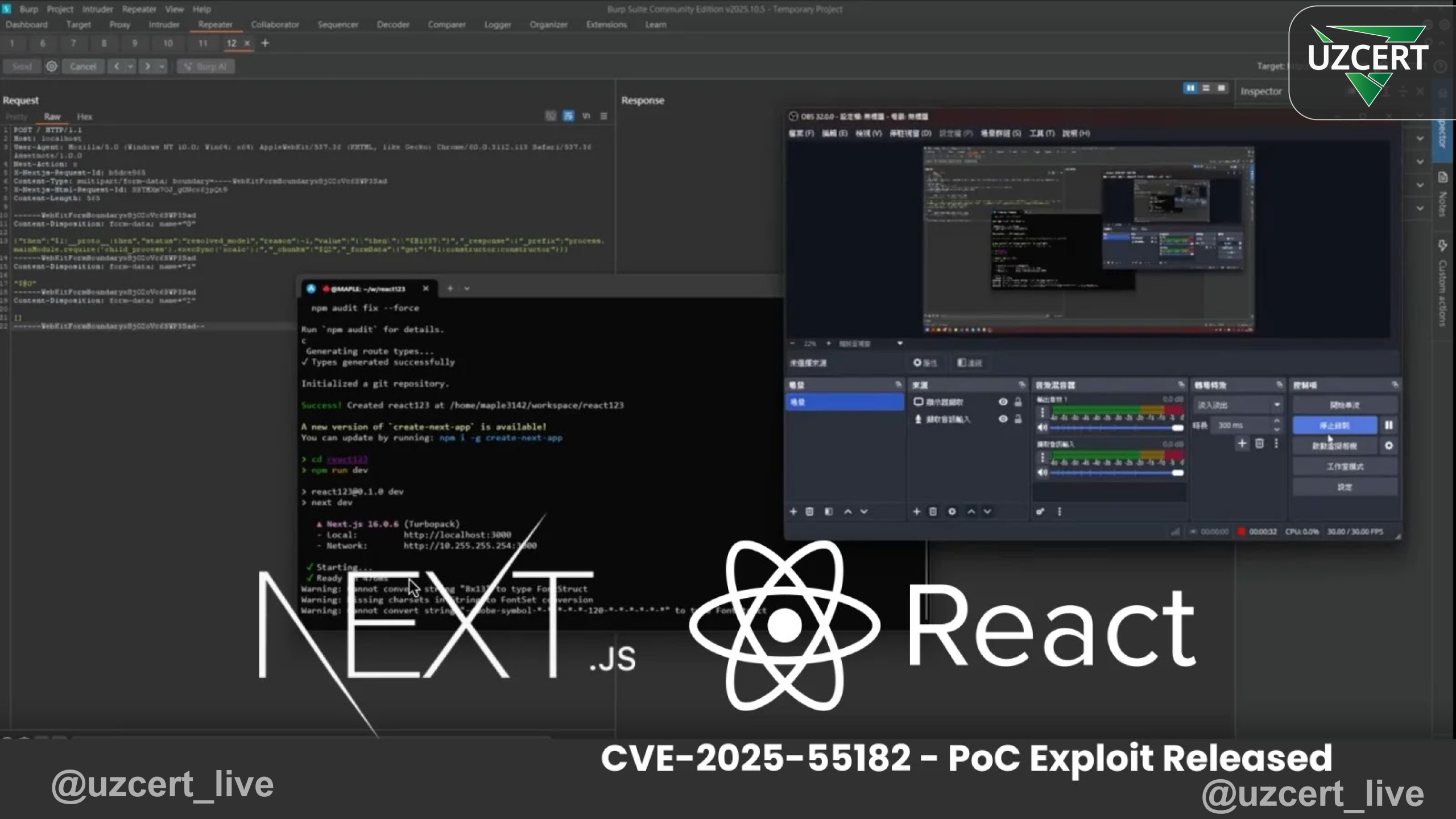
Security researcher @maple3142 demonstrated that a simple multipart HTTP request is enough to execute Node.js code on the server. In the demo, the exploit launches a child process and opens the Linux calculator without any authentication.
The attack abuses insecure deserialization within the React Flight protocol. Malformed or intentionally crafted objects are passed to the server as valid, allowing attackers to execute arbitrary code or tamper with server-side logic.
How Was the Vulnerability Discovered?
Researcher Lachlan Davidson identified the flaw and officially reported it to Meta and Vercel on November 29.
On December 3, the details were made public, after which developers immediately began releasing patches.
A specialized scanning tool was also introduced to detect vulnerable endpoints.
Have Real Attacks Already Begun?
According to Amazon Threat Intelligence, within just a few hours of public disclosure, the China-linked threat group Earth Lamia began attempting to exploit the vulnerability.
Wiz Research scanned more than 968,000 servers and found that 39% were affected.
Palo Alto Networks noted that the attack can be executed with a single crafted POST request, with near 100% reliability.
Why Is This So Dangerous?
- No authentication is required for exploitation.
- The flaw exists even in default React/Next.js configurations.
- Extensive global use of RSC dramatically widens the attack surface.
- Successful exploitation can lead to full server compromise, data theft, malicious code injection, and more.
Recommended Actions
Developers and system administrators should urgently take the following steps:
- Update React to version 19.2.1 or later, and update Next.js to the latest available release.
- Audit all endpoints related to RSC.
- Review server logs for suspicious multipart POST requests and unusual Flight objects.
- Enable additional protection rules for the Flight protocol in WAF/IDS/IPS systems.
- Require automated vulnerability scanning in CI/CD pipelines.
The CVE-2025-55182 vulnerability is one of the most severe issues seen in the React and Next.js ecosystem in recent years, and the public release of the PoC has greatly amplified the risk. Server-side rendering…



