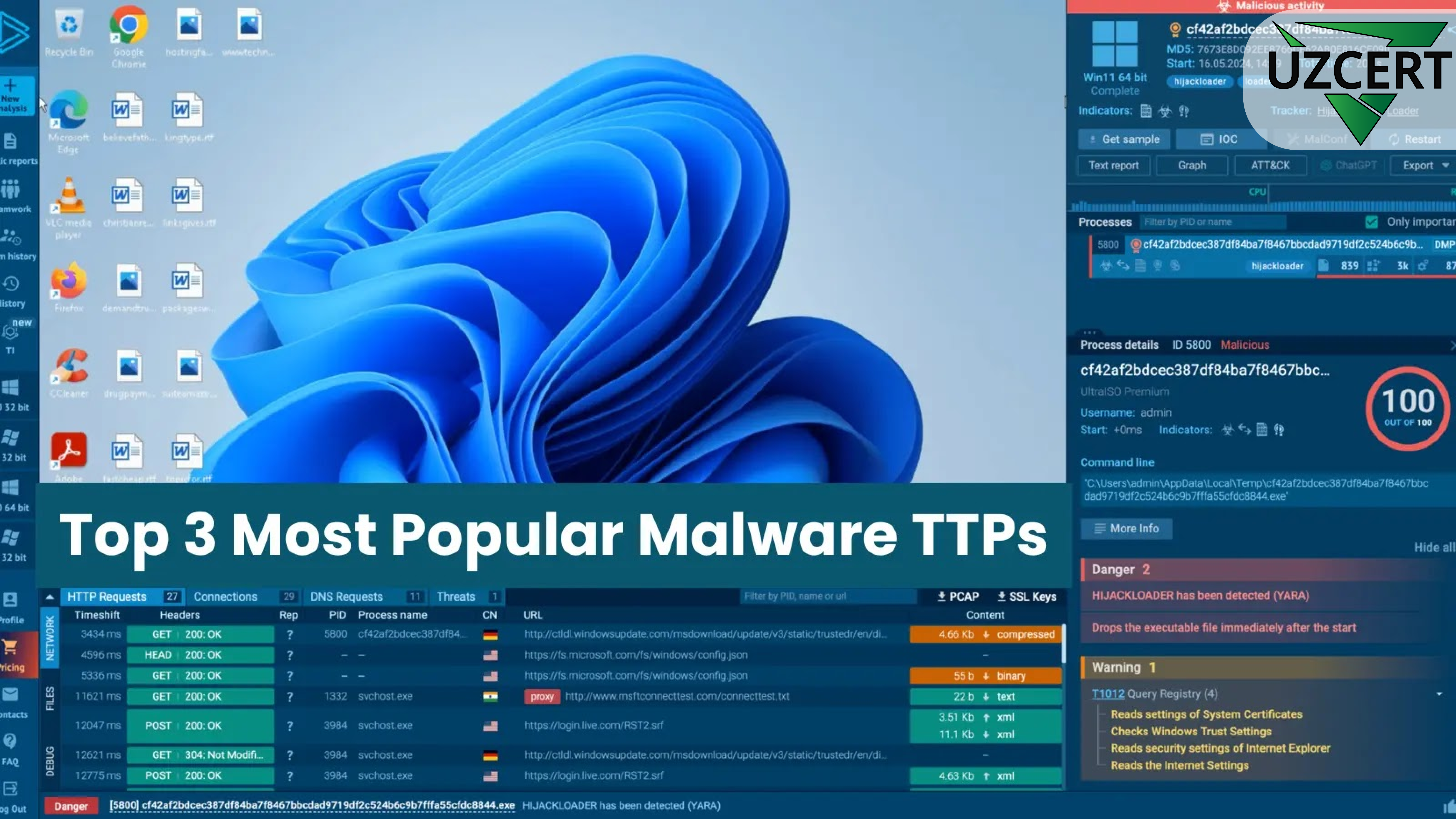
Top 3 Most Popular Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) of 2024: New Methods of Cyberattacks
In the world of cybersecurity, threats are evolving at an incredible pace. However, some attack methods stand out due to their widespread use and high effectiveness. In its 2024 report, ANY.RUN identified the most commonly used Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) by cybercriminals. In this article, we will explore the top three TTPs, how they work, and real-world examples using an interactive sandbox.
1. Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell and CMD
TTP: T1059.001 (PowerShell) and T1059.003 (CMD)
PowerShell and Command Prompt (CMD) are powerful tools built into Windows. They are typically used for system management and scripting. However, hackers exploit them for malicious purposes, such as executing harmful commands and scripts.
Why are these tools effective for hackers?
- These tools are trusted by the operating system, allowing them to bypass security measures.
- They enable the execution of commands, downloading of files, and management of processes without requiring external programs.
How do hackers use them?
- Executing malicious scripts: Hackers use PowerShell to run scripts directly in memory, which helps evade antivirus detection. CMD is used to manage files or establish network connections.
- “Living Off the Land” (LOLBins): Hackers leverage trusted tools like PowerShell and CMD to blend malicious activity with normal system operations.
- Obfuscation and automation: Scripts are often obfuscated to avoid detection and are used to automate tasks such as lateral movement or data exfiltration.
Real-world example:
Hackers send a phishing email to a user containing a password-protected ZIP file. Inside the file is a document labeled “Invoice” that prompts the user to enable macros. When macros are enabled, a PowerShell script is executed, downloading a malicious file from a remote server. This file is then executed, initiating the next stage of the attack.
2. Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion: Time-Based Delays
TTP: T1497.003
Time-based evasion is a technique where malware introduces deliberate delays to avoid detection in sandbox environments. By “sleeping” for a specific period, malware can outlast the short runtime of many automated analysis systems, ensuring its malicious activity goes unnoticed.
Why is this effective?
Sandboxes often operate within limited timeframes to analyze program behavior. By introducing delays, malware can remain inactive until the analysis window has passed, effectively concealing its malicious intent.
How do hackers use it?
- Introducing delays: Malware uses commands like
sleepto pause execution for several seconds or minutes. - Combining with other techniques: Time-based delays are often combined with obfuscation or other evasion methods.
Real-world example:
The DarkCrystal RAT malware uses a sleep command for 10 seconds before proceeding to the next stage of its attack. This helps it evade detection in sandboxes with short analysis times.
3. Masquerading: Use of Trusted Binaries
TTP: T1036.003
Masquerading is a technique where malicious files are disguised as legitimate programs. Hackers modify trusted system binaries to use them for malicious purposes.
Why is this effective?
- Trusted binaries are considered safe by the operating system and antivirus software.
- Antivirus programs and system checks often overlook such files unless suspicious behavior is detected.
How do hackers use it?
- Copying and renaming files: Hackers copy legitimate files (e.g.,
regsvr32.exe) into temporary folders like%temp%and inject malicious code into them. - Execution without elevated privileges: Modified files can be executed without requiring administrative rights, allowing them to bypass checks.
Real-world example:
The Lokibot malware copies the legitimate system file RegSvcs.exe into the folder C:\Users\admin\AppData\Roaming\F3F363\ and renames it to 3C28B3.exe. It then executes this file with injected malicious code to avoid detection.
Understanding the Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) used by attackers helps organizations strengthen their defenses and respond quickly to threats. With interactive solutions like ANY.RUN, identifying TTPs becomes easier and faster. The sandbox allows real-time monitoring of malware behavior, while tools like ATT&CK help analyze attacks and take protective measures.
Tip: In cybersecurity, a proactive approach is key to success. Regularly updating systems, training employees, and using advanced security solutions can help organizations defend against cyberattacks.



